You’ve heard about Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA) careers – maybe from a friend, a job posting, or while researching ways to help children with autism.
The field sounds promising, but the acronyms are confusing. ABA vs RBT?, BCBA vs RBT? What Do They Mean?
More importantly, which career path makes sense if you’re starting from scratch?
That’s what we’re covering in this blog.
This guide breaks down ABA vs RBT and RBT vs BCBA, including salary averages, actual timelines, and precise requirements.
You’ll understand what each role entails on a day-to-day basis, the level of investment required, and which one best fits your current situation.
Let’s dive in.
Overview of ABA and Behaviour Analysis Careers

Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA) refers to the use of scientific methods to modify behaviours. ABA professionals teach new skills and reduce problem behaviours by breaking them into smaller steps, collecting data, and adjusting methods based on results.
For example, a child with autism may learn to brush their teeth through small steps, such as picking up the toothbrush, applying toothpaste, brushing in sections, and then receiving positive reinforcement after each success.
ABA professionals work in schools, ABA clinics, clients’ homes, hospitals, telehealth platforms, and residential facilities.
ABA isn’t just for autism, though ABA vs RBT often gets framed in that context. ABA is used with clients who have:
- Developmental disabilities
- Intellectual disabilities
- Behavioural disorders
- ADHD
- Anxiety disorders
- Traumatic brain injuries.
ABA operates on three core principles.
- Reinforcement increases desired behaviours by adding rewards or removing negatives.
- Extinction decreases problem behaviours by removing their rewards.
- The Antecedent-Behaviour-Consequence (ABC) model identifies what triggers behaviours and what maintains them.
These principles originated from B.F. Skinner’s experimental psychology work in the 1930s and 1940s.
Researchers Baer, Wolf, and Risley applied them to human behaviour in the 1960s.
Ivar Lovaas explained the effectiveness of ABA in autism treatment in the 1970s.
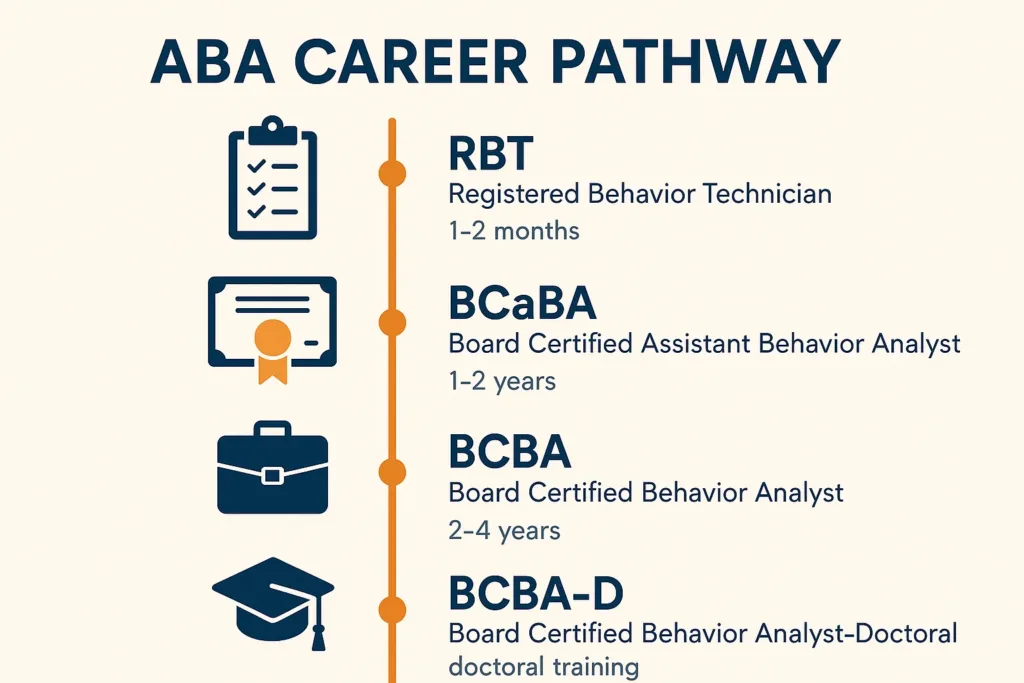
The career path offers clear progression:
Entry → RBT → BCaBA → BCBA → BCBA-D
Registered Behaviour Technician (RBT) Role
A Registered Behaviour Technician (RBT) is a paraprofessional who implements behaviour intervention plans under direct BCBA supervision.
ABA vs RBT comparisons can often confuse newcomers, but they are actually quite simple. ABA means the field, while RBT is a specific certification within it.
ABA professionals teach new skills and reduce problem behaviours by breaking them into smaller steps, collecting data, and adjusting methods based on results.
They implement specific protocols designed by BCBAs, such as teaching communication skills through trial training or helping clients practice social interactions.
To learn about the training requirements for RBTs, read this blog.
The certification timeline is 4-8 weeks total.
Training programs typically take 2-4 weeks to complete, followed by 1-2 weeks to schedule and complete the competency assessment, then immediate exam scheduling after passing the assessment.
RBTs work in:
- Public and private schools
- ABA therapy clinics
- Clients’ homes for in-home services
- Telehealth platforms.
The national average RBT salary is $54,000 per year, with hourly rates averaging around $ 26.40. Entry-level positions start around $37,000, while experienced RBTs can earn up to $45,000 annually.
RBTs work under strict supervision requirements.
BCBAs must directly observe RBTs for 5% of their monthly client contact hours. This means that an RBT working 40 hours per week receives approximately 8 hours of direct supervision per month.
If you’re thinking about becoming an RBT, try our free practice test first. It helps you assess your readiness and identify areas where you may need to focus your studies.
Board Certified Behaviour Analyst (BCBA) Role
A Board Certified Behaviour Analyst (BCBA) is a master’s-level independent practitioner who designs, supervises, and evaluates ABA interventions.
The BCBA vs RBT comparison shows a clear distinction. Unlike RBTs, who implement existing plans, BCBAs create comprehensive treatment strategies and make clinical decisions.
BCBAs conduct functional behaviour assessments to identify why problem behaviours occur, then develop individualised treatment plans based on their findings.
They supervise RBTs and other support staff, providing training and ongoing oversight.
BCBAs also perform direct therapy services for complex cases and evaluate treatment effectiveness through data analysis.
The educational path requires significant commitment.
Candidates must earn a master’s degree in ABA, psychology, education, or a related field that includes a Verified Course Sequence (VCS) – specific BACB-approved coursework covering behaviour analysis principles.
They must complete 2,000 supervised fieldwork hours (or 1,500 concentrated hours) under the supervision of an experienced BCBA, then pass the comprehensive BCBA board examination.
The certification timeline spans 3-5 years total.
- Master’s programs with required coursework take 2-3 years.
- Fieldwork hours require 6-18 months.
- Exam preparation takes 3-6 months.
BCBAs must maintain their BACB certification through continuing education and adherence to ethical standards.
Many states also require separate licensure for independent practice, adding additional requirements and fees.
The national average is $102,371 annually, with variations by location. California averages $108,700, while Florida averages $63,573. Experienced BCBAs in leadership roles can earn significantly more.
BCBAs can advance their careers in the following fields:
- Clinical supervision roles
- Program director positions
- School district behaviour specialists
- Private practice ownership
- Consulting services.
Some BCBAs specialise in organisational behaviour management or pursue doctoral degrees for research and university teaching.
Key Differences: BCBA vs RBT
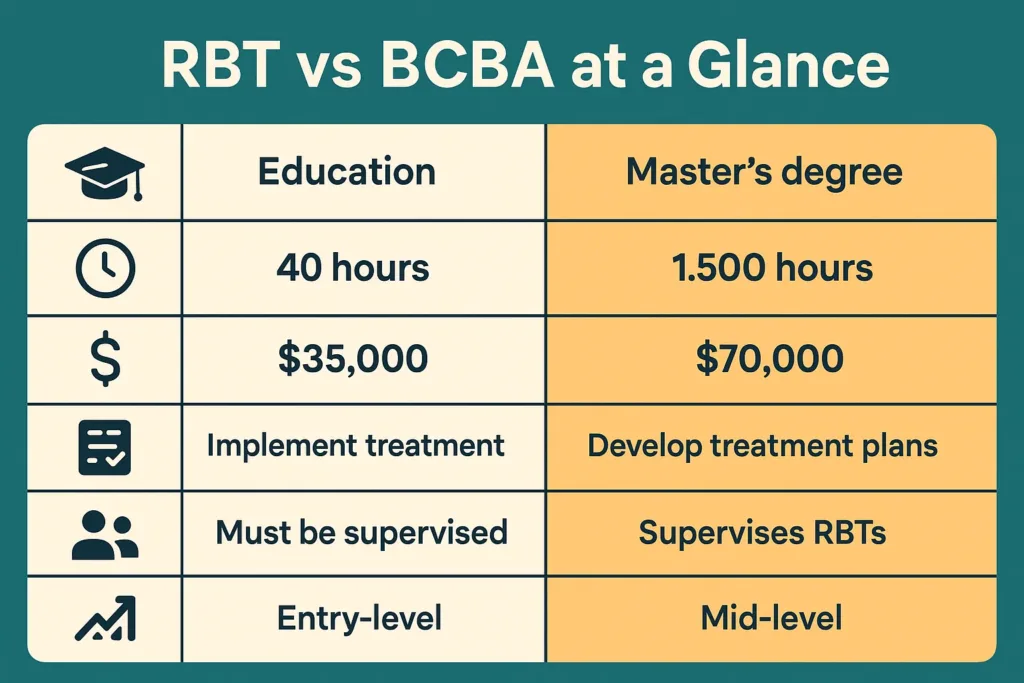
Now let’s explore the BCBA vs RBT distinction:
| Factor | RBT | BCBA |
| Education Required | High School Diploma | Master’s degree |
| Career Level | Entry-level | Mid-career professional |
| Training Time | 40 hours + 4-8 weeks | 2,000+ hours + 3-5 years |
| Coursework | Basic RBT training program | Verified Course Sequence (VCS) |
| Role Function | Implements existing plans | Creates plans and supervises |
| Supervision | Receives 5% monthly supervision | Provides supervision to RBTs |
| Salary | $54,000 average | $102,371 average |
| Daily Work | Direct client implementation | Assessment, planning, and staff training |
When examining ABA vs RBT roles specifically, remember that ABA includes the entire scientific approach, while RBT represents one certification level within the ABA framework. Similarly, the BCBA vs RBT comparison shows the progression from implementing ABA techniques to designing and supervising them.
How To Choose The Right Career Path: RBT vs BCBA
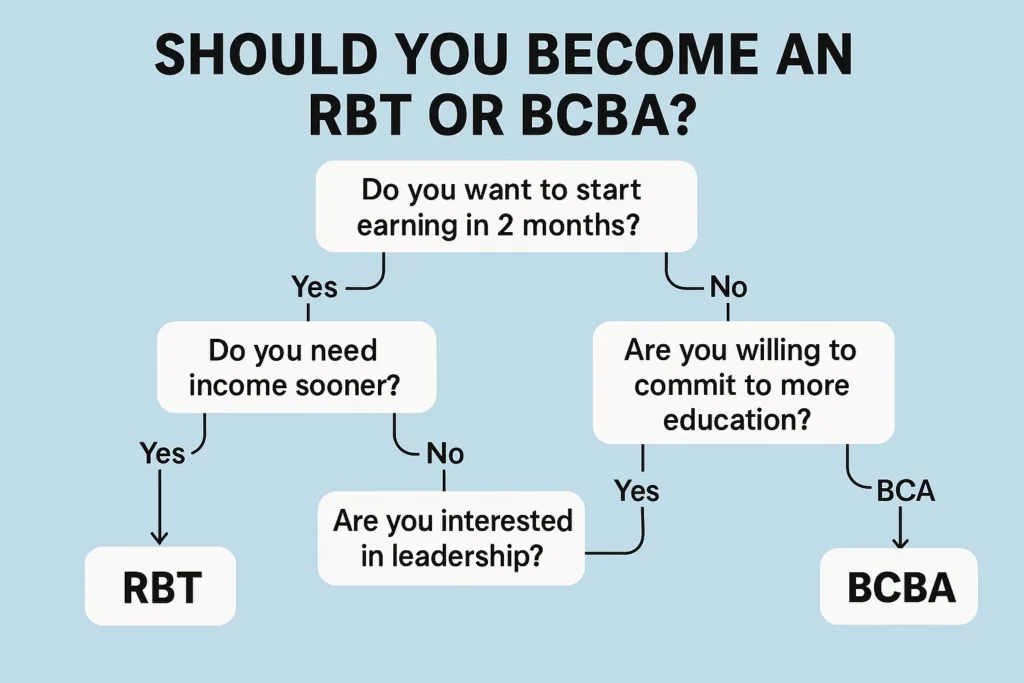
Consider your work preferences.
- If you enjoy hands-on client interaction and implementing structured activities, a career as an RBT may be a good fit for you.
- If you prefer strategic thinking, problem-solving, and leading teams, BCBA roles are a better fit for your strengths.
Evaluate your comfort with education requirements.
RBTs require basic training and ongoing supervision, whereas BCBAs must complete graduate-level coursework and demonstrate the ability to make independent decisions.
Consider your tolerance for extensive client interaction. RBTs spend 80-90% of their time with clients, while BCBAs split their time between clients, supervision, and administrative tasks.
Time & Cost Investment
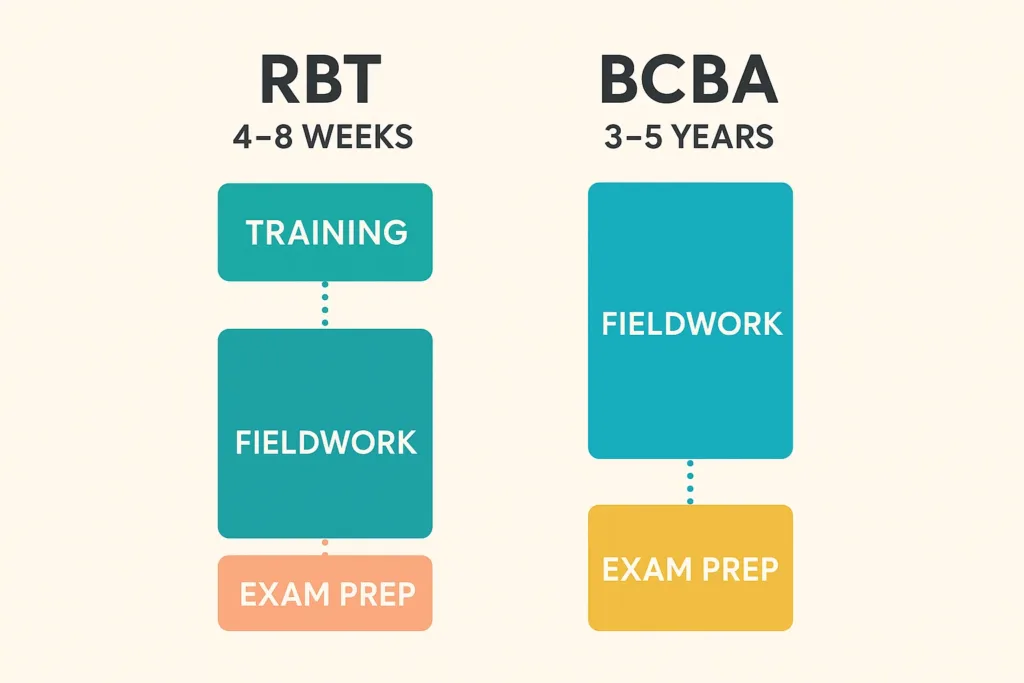
| Factor | RBT Investment | BCBA Investment |
| Time | 4-8 weeks to certification | 3-5 years to certification |
| Cost | $500-$1,500 for training and exam | $30,000-$80,000 for a Master’s degree |
| Earning Potential | $54,000 average | $102,371 average |
Action Plans
Steps to Become an RBT:
- Verify high school diploma/GED completion
- Research BACB-approved 40-hour training providers
- Complete RBT training program
- Find a supervising BCBA for competency assessment
- Pass RBT Competency Assessment
- Register for and pass the RBT certification exam
- Complete background check
- Apply for RBT positions
Steps to Become a BCBA:
- Research master’s programs with Verified Course Sequence (VCS)
- Apply and enrol in an accredited graduate program
- Complete the required behaviour analysis coursework
- Secure supervised fieldwork placement (2,000 hours minimum)
- Accumulate supervised experience while completing coursework
- Apply for the BCBA board examination
- Pass the BCBA certification exam
- Apply for state licensure (if required in your state)
- Seek BCBA employment or start private practice
Final thoughts on ABA vs RBT
The RBT vs BCBA decision comes down to three factors: time, money, and professional goals.
Choose RBT if you need income quickly, prefer hands-on client work, and want to test the ABA field before committing long-term.
Choose BCBA if you can invest 3-5 years and $30,000-$80,000 in education for nearly double the salary ($102,371 average) and leadership opportunities. The upfront cost pays back within 2-3 years through higher earnings.
Remember: RBT isn’t a dead end. Many successful BCBAs began their careers as RBTs, using their experience to fund their master’s degrees and gain insight into the field’s realities before advancing.
Your next step depends on the path you have chosen. If you’re leaning toward RBT, start with our free RBT practice test to assess your readiness and identify knowledge gaps before committing to training. It takes 15 minutes and shows precisely what you need to study.
If BCBA appeals to you, research master’s programs with Verified Course Sequences in your area this week. Don’t wait – program deadlines fill up fast.


